In the world of emergency medicine, time is of the essence. Every second counts when it comes to saving lives, especially in cases of cardiac arrest. The Lucas device has emerged as a groundbreaking tool that aims to improve survival rates during these critical moments. If you’re unfamiliar with the Lucas devices’ this article will provide you with an in-depth understanding of how it works, its applications, and why it’s becoming a game-changer in emergency medical care.
What is the Lucas Device?
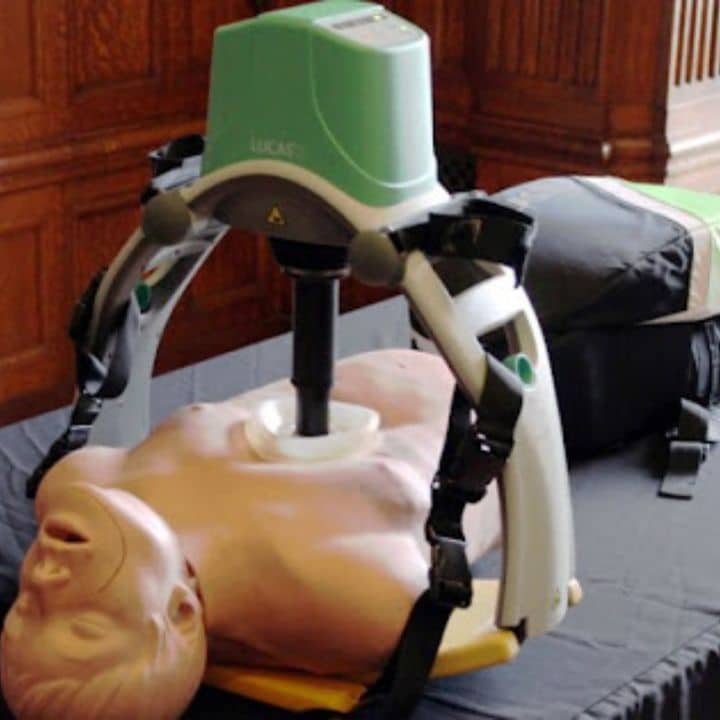
The Lucas device is a mechanical chest compression system designed to provide consistent, high-quality chest compressions during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
Unlike manual CPR, which requires human intervention, the Lucas device automates the process, ensuring the right depth and rate of compressions. This reduces the chance of human error and helps increase the chances of survival for individuals who experience sudden cardiac arrest.
How Does the Lucas Device Work?
The Lucas device operates through a combination of mechanical components that provide consistent chest compressions. The device consists of a base unit, a compression mechanism, and a pneumatic piston. These compressions are vital in maintaining circulation to vital organs, especially the brain, until further medical assistance arrives.
One of the key features of the Lucas devices’ is its ability to deliver continuous, uninterrupted compressions. Traditional CPR requires pauses for mouth-to-mouth ventilation or for rescuers to tire, which can reduce the effectiveness of chest compressions. The Lucas devices’ ensures that the chest compressions are sustained, leading to better outcomes in cardiac arrest situations.
The Science Behind the Lucas Device
When a person goes into cardiac arrest, the heart stops pumping blood to the body, depriving vital organs of oxygen. Chest compressions are crucial because they help manually pump the heart, restoring circulation to the brain and other organs. Research has shown that high-quality chest compressions, delivered at a consistent rate and depth, can significantly improve the chances of survival.
The Lucas device has been meticulously engineered to deliver the ideal depth of compressions—at least 5 cm (2 inches) deep—at a rate of around 100-120 compressions per minute. This conforms to the American Heart Association’s guidelines for effective CPR. By automating this process, the Lucas device ensures that the patient receives optimal care during critical moments, even if healthcare professionals are unable to provide manual compressions.
Advantages of Using the Lucas Device
- Consistency and Accuracy
One of the main advantages of the Lucas devices’ is its ability to deliver consistent and accurate compressions. Unlike manual CPR, where the effectiveness can vary based on the rescuer’s fatigue or technique, the Lucas device provides uniform pressure and pace, reducing the variability and increasing the chances of a successful resuscitation. - Reduces Rescuer Fatigue
Performing manual chest compressions for extended periods can be physically exhausting, especially in challenging environments like an ambulance or during transport. The Lucas device takes over the labor-intensive task of compressions, allowing emergency medical teams to focus on other critical interventions such as administering medications or preparing the patient for transport to the hospital. - Improved Outcomes in Remote Locations
In remote or hard-to-reach areas where advanced medical facilities are not immediately available, the Lucas device provides an essential tool for paramedics and emergency responders. - Helps with Transport and Stabilization
When transporting a patient to the hospital, especially in cases of sudden cardiac arrest, it can be difficult to maintain proper CPR. The Lucas device allows medical teams to stabilize the patient during transport, which is essential in improving survival rates and reducing the risk of neurological damage caused by a lack of oxygenated blood flow to the brain. - Clinical Evidence and Research Support
Numerous studies have supported the efficacy of the Lucas device in improving survival outcomes for cardiac arrest patients. Research has shown that the use of the Lucas device leads to better adherence to CPR guidelines, better blood circulation, and, ultimately, higher rates of survival. This evidence solidifies the importance of incorporating the device into emergency medical protocols.

Read more: Respawn Gaming Chair
Applications of the Lucas Device
The Lucas devices’ is primarily used by paramedics, emergency medical technicians (EMTs), and hospital emergency teams in situations where rapid, high-quality chest compressions are critical. Here are some of the main applications of the Lucas device:
- Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest (OHCA)
When a patient suffers a cardiac arrest outside of a hospital setting, the Lucas device can be used by emergency responders to maintain circulation until the patient can be transported to a medical facility. - In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
Hospitals use the Lucas device during code blue situations where a patient’s heart has stopped. It provides reliable and continuous compressions, allowing hospital staff to focus on other life-saving measures. - Air Transport and Critical Care
The Lucas devices’ is a valuable tool for air ambulance services and critical care transport teams. It ensures that compressions are continuous and effective even during flight, where maintaining manual CPR can be challenging due to turbulence or limited space. - High-Risk Environments
In high-risk environments like rescue operations, remote locations, or disaster zones, the Lucas device provides emergency teams with an effective tool for saving lives while reducing the physical burden on rescuers.
The Future of the Lucas Device in Emergency Medicine
As technology continues to advance, the Lucas devices’ is likely to see further improvements. In the future, it may integrate with other medical technologies such as defibrillators or advanced monitoring systems, providing emergency responders with a more comprehensive tool for managing cardiac arrest cases. Additionally, with the increasing use of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring, the Lucas device could potentially be monitored and adjusted in real-time by medical professionals at a distance, ensuring optimal performance and patient care.
Conclusion
The Lucas devices’ is an essential innovation in emergency medicine that helps save lives during cardiac arrest. By providing consistent, high-quality chest compressions, the device improves survival rates and outcomes for patients in both pre-hospital and hospital settings. With its ability to reduce rescuer fatigue, deliver uninterrupted CPR, and function in remote environments, the Lucas devices’ is a critical tool for emergency responders worldwide.
As medical technology continues to evolve, we can expect the Lucas devices’ to become an even more integral part of cardiac arrest management, ultimately helping to save countless lives in the years to come. If you’re involved in emergency medical care or are simply interested in the latest advancements in health technology, understanding the Lucas devices’ is a step toward improving the future of healthcare.